What is a Mutation?
A mutation is a change in the structure of the gene that results in a different phenotype.
There are four types of mutation:
- Substitution: This is where one or more bases in the chain of DNA is substituted for another. When a single base is changed, this is called a point mutation.
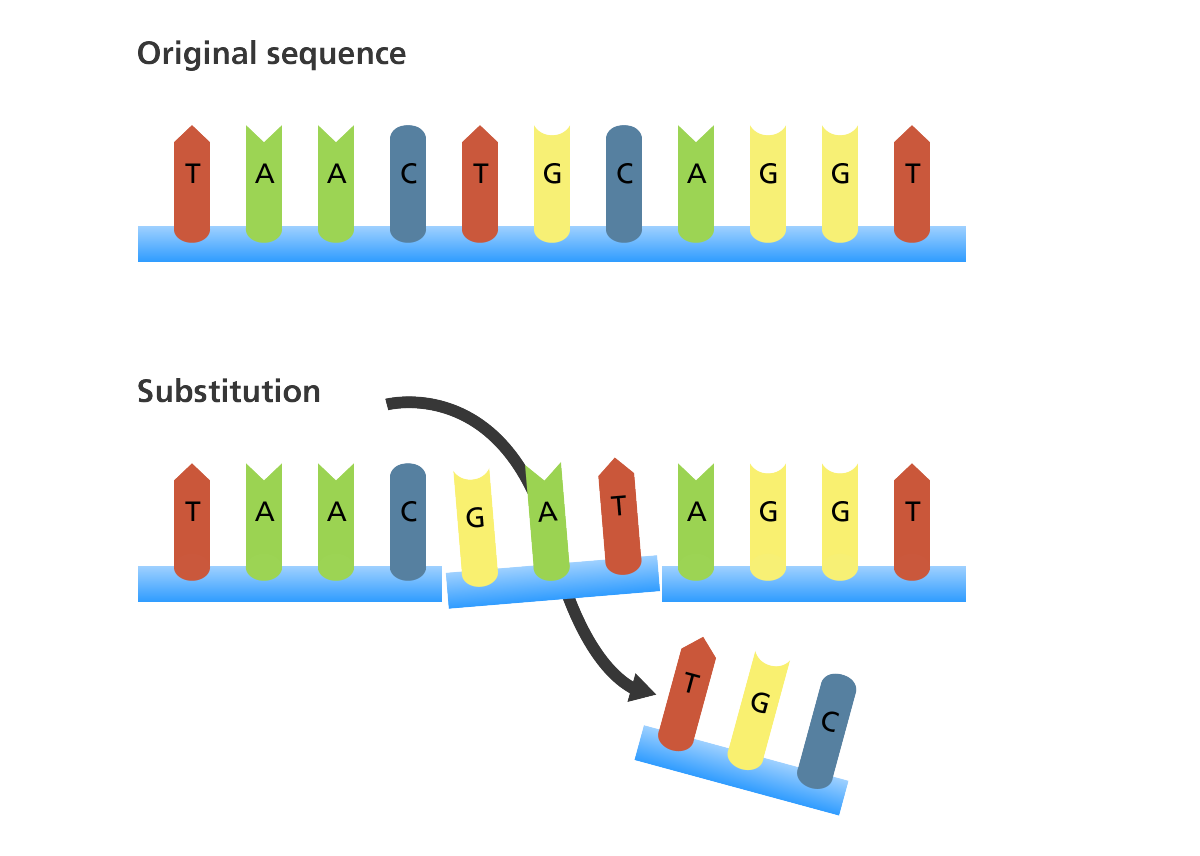
- Deletion: This is where one or more base pairs are deleted and not replaced. When this happens in one place, it is also a point mutation.

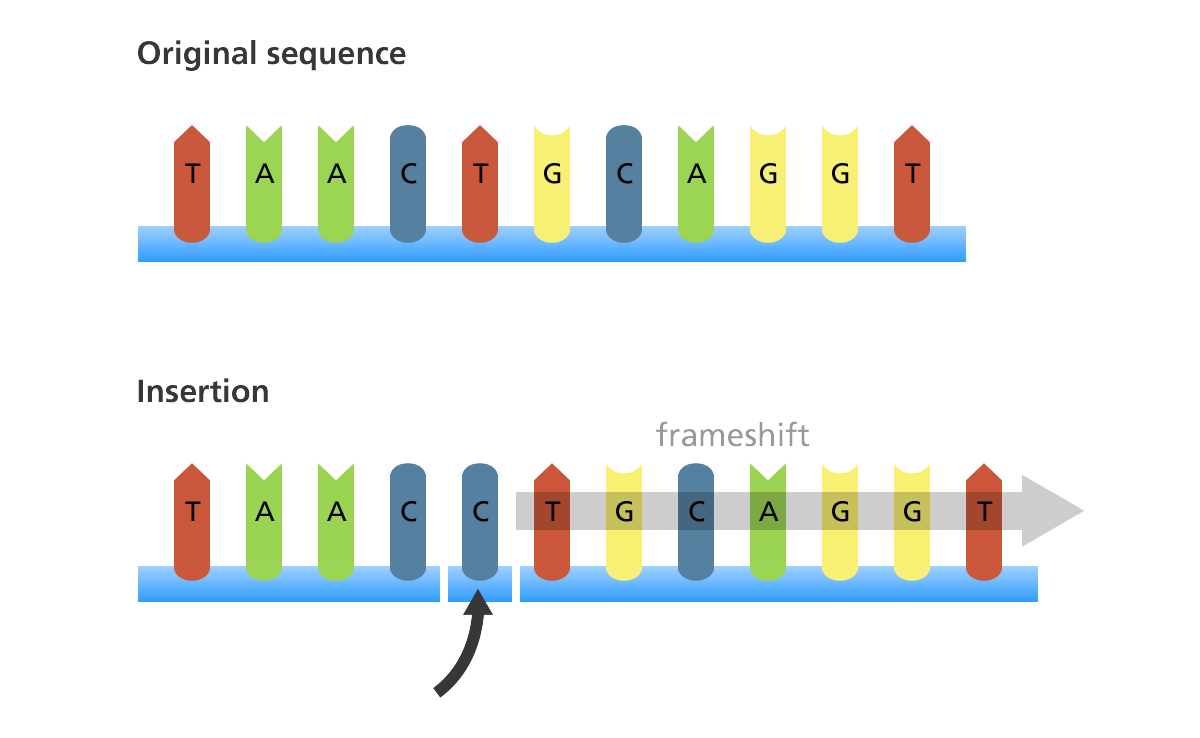
- Insertion: This is when an extra base is added to the chain and causes a frameshift, meaning the bases following are moved from their original placing.
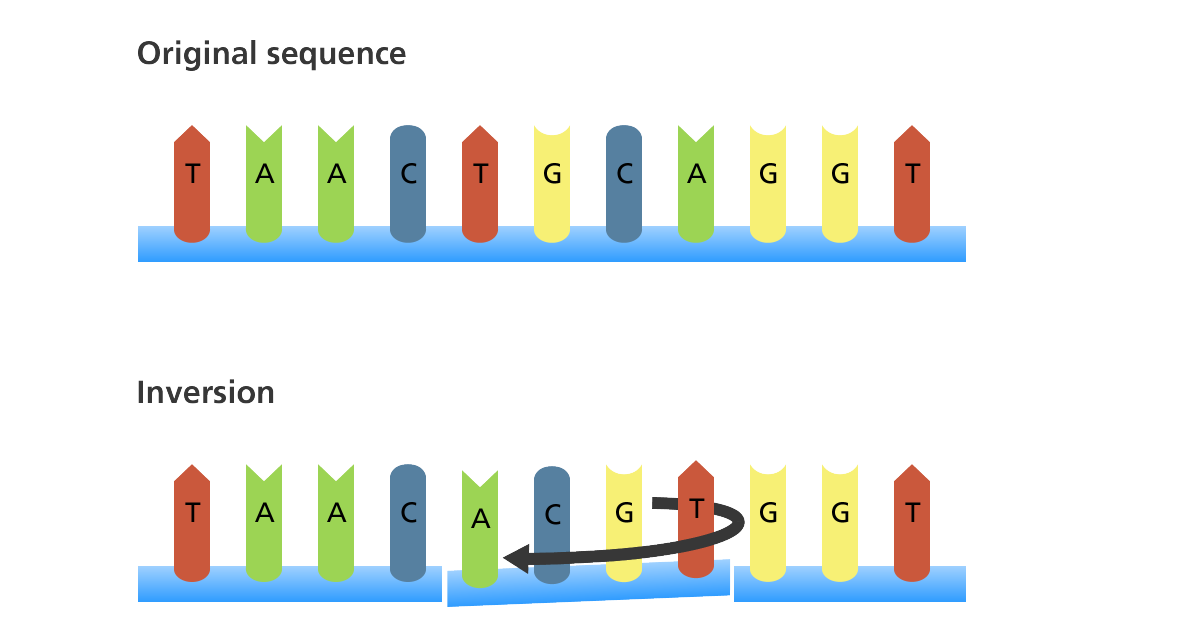
- Inversion: This is when a segment of bases is reversed.
What Causes Mutation
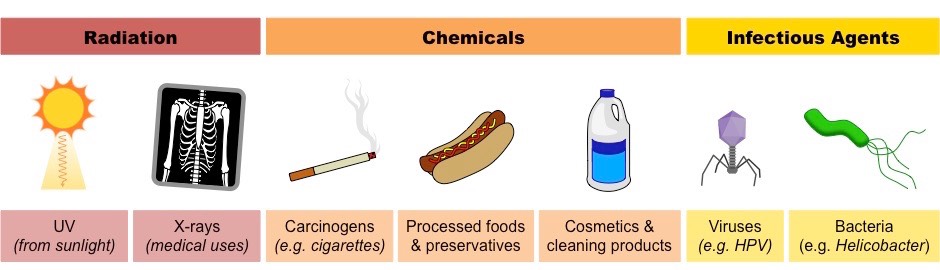
Mutations can be caused by things called mutagens, which are in the environment and cause mutations. The 3 different types of mutagens are:
- Chemical
- Physical
- Biological
Genetic or Not?
Some mutations are genetic, meaning that they can be passed from family to family. Some mutation however, can come from the environment.
